Binary Tree Maximum Path Sum | Leetcode 124 | Binary Tree | Dynamic programmin
A path in a binary tree is a sequence of nodes where each pair of adjacent nodes in the sequence has an edge connecting them. A node can only appear in the sequence at most once. Note that the path does not need to pass through the root.
The path sum of a path is the sum of the node's values in the path.
Given the root of a binary tree, return the maximum path sum of any non-empty path.
Example 1:
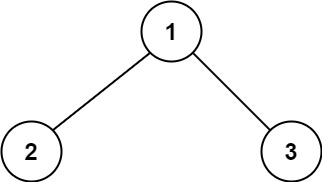
Input: root = [1,2,3]
Output: 6
Explanation: The optimal path is 2 -> 1 -> 3 with a path sum of 2 + 1 + 3 = 6.
Example 2:
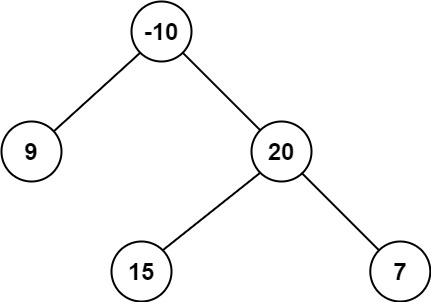
Input: root = [-10,9,20,null,null,15,7]
Output: 42
Explanation: The optimal path is 15 -> 20 -> 7 with a path sum of 15 + 20 + 7 = 42.
Constraints:
The number of nodes in the tree is in the range
[1, 3 * 10<sup>4</sup>].-1000 <= Node.val <= 1000
Solution:
For each node, find the maximum path sum from left side, right side and the current node => "currentNodeSum"
- Compare and store the maximum value of "maxResult" and "currentNodeSum"
- Return the maximum value of left and right, and the current node
public class TreeNode { int val; TreeNode left; TreeNode right; TreeNode() {} TreeNode(int val) { this.val = val; } TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) { this.val = val; this.left = left; this.right = right; } } class Solution { private int maxSum = Integer.MIN_VALUE; private int recursion(TreeNode root) { if(root == null) return 0; int left = Math.max(recursion(root.left ), 0); int right = Math.max(recursion(root.right), 0); int currentNodeSum = root.val + left + right; maxSum = Math.max(maxSum, currentNodeSum); return Math.max(left,right) + root.val; } public int maxPathSum(TreeNode root) { int res = recursion(root); return Math.max(maxSum, res); } }